Since 2005, the number of renters in this country has gone up 9 million, to 41 million, the biggest surge of any decade on record. That brings the share of renting households to 37 percent, the highest in half a century. Meanwhile, their rents are up and their incomes are down: From 2001 to 2014, rents rose 7 percent (above inflation) and incomes dropped by 9 percent.
The biggest increase in renter households, surprisingly, came from the Baby Boomer cohort – people in their 50s and 60s. In fact households 40 and older make up the majority of renters.
These are among the findings in “America’s Rental Housing,” a 44-page study out this week from Harvard’s Joint Center for Housing Studies.
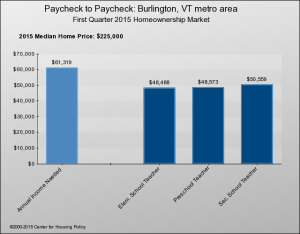
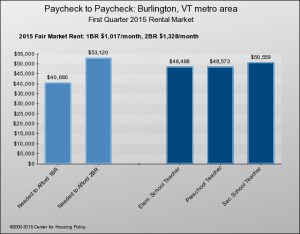
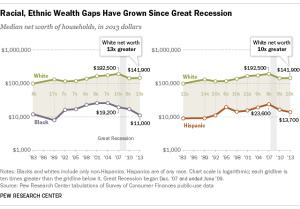
Not only are there many more renters, but many more of those renters can’t comfortably afford to live where they do. In 2014, 49 percent of renters were “burdened” (meaning they paid more than 30 percent of their incomes for rent and utilities) and 26 percent were “severely burdened” (more than 50 percent). According to Vermont Housing Data, Vermont’s current rates are a tad higher: 52.5 percent and 26.4 percent.
Yes, the housing burden falls most heavily on low-income people, but it’s growing among the middle-income stratum as well:
“(T)he sharpest growth in cost-burdened shares has been among middle-income households. The share of burdened households with incomes in the $30,000–44,999 range increased from 37 percent in 2001 to 48 percent in 2014, while that of households with incomes of $45,000–74,999 nearly doubled from 12 percent to 21 percent. Regardless of income level, though, the shares of cost-burdened households reached new peaks in 2014 among all but the highest-income renters.”
Meanwhile, only about one-fourth of eligible lower-income households receive housing assistance (Section 8 vouchers are not an entitlement!); funding for HUD’s three biggest rental assistance programs is about the same (corrected for inflation) as it was seven years ago, when the economy crashed; and the HOME program, a major source of federal funding for housing programs, has been cut way back. Private developers continue to add to the multi-family housing supply, but most of the recent additions “serve the higher end of the market,” according to the report. As it happens, high-income households (annual $100,000 or more) represent a small but fast-growing share of the rental market.
The report asserts:
“The challenge now facing the country is to ensure that a sufficient and appropriate supply of rental housing is available for a diversity of households and in a diversity of locations. While the private market has proven capable of expanding the higher-end rental stock, developers have only limited opportunities to meet the needs of lowest income households without subsidies that close the large gap between construction costs and what these renters can afford to pay. In many high-cost markets, moderate-income households face affordability challenges as well.”
“Diversity of locations” is an invocation of AFFH (affirmatively furthering fair housing) and the goal of ensuring that a good share of affordable housing is in “high-opportunity” neighborhoods,” as in what follows:
“Policymakers urgently need to consider the extent and form of housing assistance that can stem the rapid growth in cost burdened households. Beyond affordability, they also need to promote development of a wider range of housing options so that more renter households can find homes that suit their needs and in communities offering good schools and access to jobs. It will take concerted efforts by all levels of government to capitalize on the capabilities of the private and not-for-profit sectors to reach this goal.”
Dare we suggest that concerted efforts have yet to be mounted, or even contemplated, by government at many levels?




















Another good option for “aging in place” is “home sharing.” Check out HomeShare Vermont for a good example.
http://www.homesharevermont.org/about-us/
“HomeShare Vermont helps people stay in their homes by connecting them with potential housemates who are looking for a place to live. While our primary goal is to help elders stay at home, we have found that people of all ages and abilities can benefit from homesharing. There are no age, ability or income restrictions to use our services. “