My Turn, From the Burlington Free Press
” … we applaud efforts in Montpelier and are excited to work with local municipalities that want to make bold investments in affordable housing, realizing that such investments are winners in accomplishing Governor Scott’s three priorities: supporting our economy, making Vermont more affordable for Vermonters, and protecting our most vulnerable community members. Several proposals have been made – we welcome all efforts that satisfy each of these three objectives.”
by Michael Monte
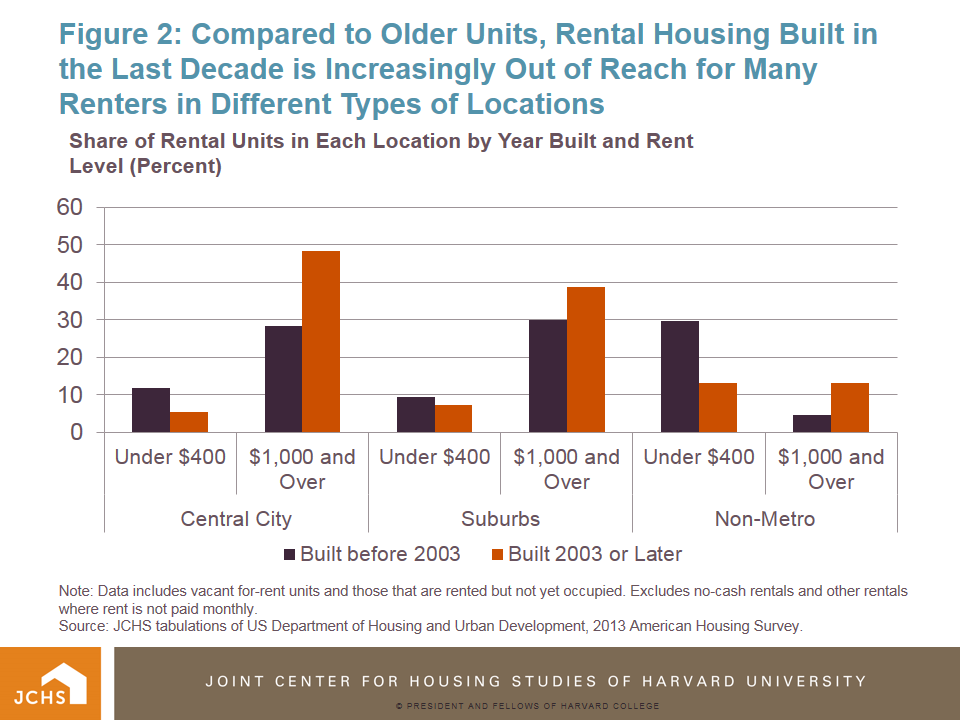
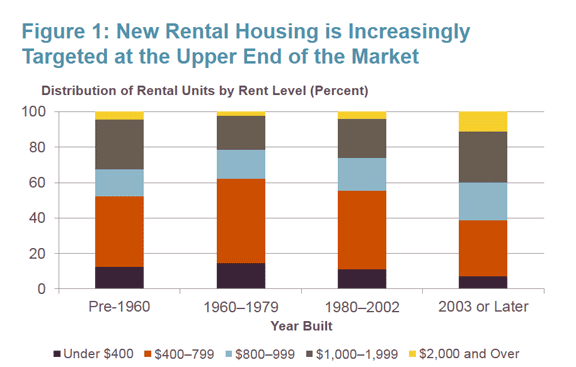
There seems to be a burst of housing construction in Chittenden County, and some are even suggesting that the tide has turned in making the rental market more affordable, or that the vacancy rate is high enough, or we’re building too fast. At the Champlain Housing Trust, our assessment is that although the trend line is improving, more needs to be done – especially for low wage earners priced out of the market, and certainly for the 350 people on any given night in the county who have no home at all.
 According to Mark Brooks, co-author of a report that provides a comprehensive semi-annual analysis of the real estate market, the long-term market vacancy rate in Chittenden County is 2%. The December, 2016 report indicated a market vacancy of 4.4% – a number offered as a point-in-time rate of what’s available without taking in consideration the timing of apartments just completing construction or other factors.
According to Mark Brooks, co-author of a report that provides a comprehensive semi-annual analysis of the real estate market, the long-term market vacancy rate in Chittenden County is 2%. The December, 2016 report indicated a market vacancy of 4.4% – a number offered as a point-in-time rate of what’s available without taking in consideration the timing of apartments just completing construction or other factors.
This lower rate is a more accurate assessment, as it takes into account the time in which newly-constructed apartments are absorbed into the market. Most will agree that a 5% rate will yield a healthy market for renters and owners alike. While we were close at a point in time in December, we’ve not sustainably reached this target.
In the last two years alone, over 1,200 apartments have been constructed. The new construction does give some renters more choices: according to the report, “…landlords are offering incentives such as one month free rent, flexible lease terms, or lower rents.” Rent rates across the board have been stable and closer in-line with inflation – unlike the previous six years.
New households are forming every day in Chittenden County, and large numbers of people are still commuting long distances from less expensive housing in more rural counties to get to work. In fact, in 2002, 73% of Chittenden County workers lived in the county; that percentage dropped to 63% in 2014. Lack of housing opportunity is leading more and more workers to commute longer distances.
Demand is still high as younger people, sometimes saddled with high college debt, are renting instead of purchasing a new home. And employers are still viewing rents and housing availability as being barriers to economic growth. A representative of one business told us recently that her company added jobs in the mid-west instead of Burlington because of the lack of housing.
In order to push the underlying market rate from 2% to a sustained 5%, we need to continue to provide additional growth. Can we sustain this growth and increase the vacancy rate in the future? We hope so. But next year fewer apartments are on track to be coming on line, less than half the number built this year. And although there are an additional 2,400 apartments in the development pipeline county-wide, those won’t be here next year, or even the year after that.

As importantly, the resources available for affordable housing are seriously limited. Although there is enormous opportunity and capacity to build more affordable housing, the equity or cash needed to insure that rents remain affordable are not available. Non-profit owners continue to struggle with meeting the demand for more affordable housing, as evidenced by long waiting lists for subsidized housing or the 150 applications CHT gets every month for the 20-25 apartments available.
That’s why we applaud efforts in Montpelier and are excited to work with local municipalities that want to make bold investments in affordable housing, realizing that such investments are winners in accomplishing Governor Scott’s three priorities: supporting our economy, making Vermont more affordable for Vermonters, and protecting our most vulnerable community members. Several proposals have been made – we welcome all efforts that satisfy each of these three objectives.
————————————————————————————————————————-
Michael Monte, is Chief Operations & Financial Officer at The Champlain Housing Trust, founded in 1984, it is the largest community land trust in the country. Throughout Chittenden, Franklin and Grand Isle counties, CHT manages 2,200 apartments, stewards 565 owner-occupied homes in its signature shared-equity program, offers homebuyer education and financial fitness counseling, provides services to five housing cooperatives, and offers affordable energy efficiency and rehab loans. In 2008, CHT won the prestigious United Nations World Habitat Award, recognizing its innovative, sustainable programs.