A new verb, or gerund, is twittering its way into the contemporary housing lexicon: “co-living.”
It’s often paired with “co-working,” another neologism, and “micro-housing.” These words are being used most commonly to describe the emerging lifestyles of highly driven, hard-striving young entrepreneurs, typically in technical fields — Millennial start-up wannabes, they’re sometimes called in the literature. Harnessed to their ambitions, they’re willing to live in tiny spaces with some common amenities (co-live), work in open-space offices where they can freely network and brainstorm with peers (co-work), and abandon the idea of maintaining a conventional “work-life balance.”
Harnessed to their ambitions, they’re willing to live in tiny spaces with some common amenities (co-live), work in open-space offices where they can freely network and brainstorm with peers (co-work), and abandon the idea of maintaining a conventional “work-life balance.”
These patterns reportedly originated in the Bay Area, as you might expect, but are showing up in New York. This summer, the Times ran a story about Pure House, one of several businesses renting apartments with amenities to such people who are willing to pay $1,600 to $4,000 a month to share rooms with others of their ilk. “The Millennial Commune,” read the headline. (For BuzzFeed’s elaboration on this phenomenon, click here.)
We’ve never met anybody like that, but we take it on faith that such people really do exist. What we’d like to suggest, though, is that some variant of co-living might have appeal for ordinary people, too – Millennials and oldsters, alike. We’ll explain in a moment, but first, let’s be clear that co-living is not the same as cohousing.
Cohousing, as the Cohousing Association of the United States describes it, is “an intentional community of private homes clustered around shared space.” There are many variations of this basic idea of combining private and communal space, and a couple of dozen of these communities have sprung up around Vermont. These are clustered developments, but they’re not necessarily adduced as an answer to the housing-unaffordability problem because of the added costs associated with the shared facilities.
Co-living, by contrast, puts people in tiny apartments (say, 200-300 square feet) with access to some shared space (such as a communal kitchen and lounge). Typically, these are furnished rentals.
An example is Commonspace, 21 micro units being developed on two floors of a five story building in Syracuse, N.Y., above a co-working office space. Each unit will have a bathroom and a kitchenette and will rent from $700 to $900 a month — supposedly slightly less than a one-bedroom apartment goes for in Syracuse, according to a fine profile in The Atlantic. 
Quite apart from the “co-working” annex, micro-units have proliferated in Seattle over the last few years and appear to appeal especially to people who want to live close by where they work.
Now obviously, this sort of place is not for everyone. It means, among other things, giving up the idea that you’ll be paying for living quarters big enough to hold all your seldom-used stuff.
But it might make sense for lots of people — recent college grads working their first jobs, dislocated workers or homeless people getting back on their feet, retirees living on fixed incomes. Not that all these people would necessarily have live together, but assorted communities might suggest themselves.
And beyond rentals, perhaps different ownership models could be devised by land trusts, using judicious public subsidies, all with an eye to affordability.









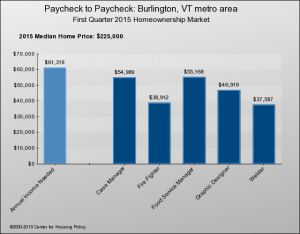
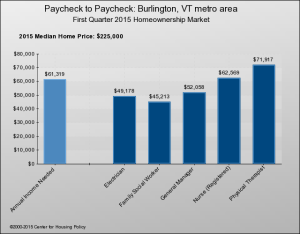
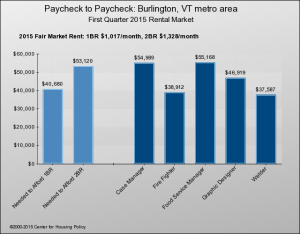
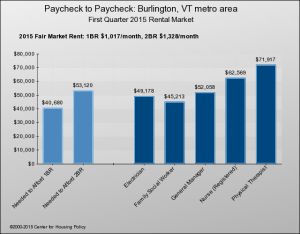
Another good option for “aging in place” is “home sharing.” Check out HomeShare Vermont for a good example.
http://www.homesharevermont.org/about-us/
“HomeShare Vermont helps people stay in their homes by connecting them with potential housemates who are looking for a place to live. While our primary goal is to help elders stay at home, we have found that people of all ages and abilities can benefit from homesharing. There are no age, ability or income restrictions to use our services. “