From: Wonkblog
By Emily Badger May 13 at 6:30 AM
Beryl Satter knew something like this was bound to happen. Or, rather, to happen again.
The Rutgers historian wrote the book on an obscure form of predatory lending from the mid-20th century that victimized black home buyers when banks would not lend them mortgages. Her book, “Family Properties,” came out in 2009, on the heels of the housing crash. And as she traveled the country talking about it — about families defrauded from the homes they thought they owned, about sellers who promised home ownership but collected deposits and evictions instead — people kept approaching her.
“Pretty much everywhere I go, people say ‘I’ve been hearing about this,'” Satter says. “Contract” lending is making a comeback.
In this model, buyers shut out from conventional lending are offered an alternative: They can make monthly payments on a home directly to the seller, instead of a bank, with the promise of receiving the deed only once the property is entirely paid off, 20 or 30 years down the road. In the meantime, they have few of the legal protections of a typical home buyer but all of the responsibilities of one. They don’t build equity with time. They can be easily evicted. And if that happens, they lose all of their investment.
According to the Detroit Free Press, more homes were bought in Detroit last year using such “land contracts” or “contracts for deeds” than conventional mortgages. In a series of recent stories, the New York Times has reported that Wall Street is now betting on this market, with investors buying foreclosed homes by the thousands and selling them on contract. Earlier this week, the Times reported that the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau is now investigating the practice’s resurgence, although it is not by definition illegal.
What is particularly alarming about the trend, though, is that we’ve seen it before. In its earlier incarnation, it was an explicitly racist form of exploitation. And now it is victimizing the same groups again: mostly lower income and minority home buyers who can’t access traditional credit.
“There’s nothing new here in the slightest,” Satter says. “This is just a continuation of the same old game. That’s what’s so disturbing.”
In the earlier era when this was common, between the 1930s and 1960s, contract lending was in some cities the primary means middle-class blacks had to buy homes. Real estate agents and speculators jacked up the price of properties two- or threefold. Then when families fell behind on a month’s payment or on repairs, they were swiftly evicted. The sellers kept their deposits and found the next family.
Satter’s father, Chicago lawyer Mark Satter, helped organize black Chicagoans to fight the practice in the 1950s. He estimated then that about 85 percent of homes bought by black in Chicago were bought on contract. “It was the way you bought,” Beryl Satter says. “There was no other way.” Many of those families then struggled to keep their homes in a system that was not sustainable by design.
Atlantic writer Ta-Nehisi Coates based his blockbuster 2014 article “The Case for Reparations”around the story of Chicago blacks who suffered under this system, the outgrowth, as he put it, of a segregated city with “two housing markets — one legitimate and backed by the government, the other lawless and patrolled by predators.”
The Times reports of what’s happening today sound eerily similar. Writers Matthew Goldstein and Alexandra Stevenson report that an estimated 3 million people have bought homes through contracts, although the numbers are hard to track given that the deals are regulated differently in each state and are not subject to the same disclosures as mortgages.
The practice is particularly common, they report, in distressed Midwestern communities like Akron and Detroit, where the government offered hundreds of foreclosed properties to investors in bulk sales. Those same investors, the Times reports, have turned around and sold the properties on contract to moderate-income buyers for sometimes four times as much.
Why now?
But why, though, would a financial scheme created in an era of sanctioned racial discrimination be making a resurgence today? Since Satter’s father tried to sue over the tactic a half-century ago, the Fair Housing Act and Home Mortgage Disclosure Act were passed. And the end of legal discrimination opened up legitimate lending to more blacks who were no longer forced into the housing market’s rapacious underworld.
But a crucial similarity between the two eras exists: Many people still can’t get loans today.
Now, this is the case because lenders have tightened their credit standards since the crash, overcorrecting for the bubble’s exuberance with historic stinginess. The Urban Institute has counted more than 5 million loans currently “missing” from the housing market — mortgages that would have been made between 2009 and 2014 if lenders used the kind of credit standards that were common back in 2001, a benchmark for more reasonable lending prior to the housing bubble.
Millions of Americans over this same time have had their credit ruined by foreclosures — in many cases because of predatory subprime lending that has now put them in the crosshairs of predatory land contracts. Minorities who were disproportionately targeted for the former are not surprisingly concentrated among those caught up in the latter.
“When the banks close down, people still need to buy,” Satter says. And so they find a way. Just as creative investors find a way to meet their demand. Land contracts are to housing whatpayday loans are to banking and Rent-A-Centers are to furniture. What people in need can’t access through credit someone is always willing to provide — for a price.
A lawyer for Harbour Portfolio Advisors in Dallas, one of the larger players in the new wave of contract lending, told the Times that the firm’s business model is “to purchase unproductive residential properties and sell them to other people who will make them productive again.” But Satter frames this differently.
“Choices that black Americans have had for housing loans have been predatory loans, or no loans,” she says. And when banks choose not to loan, she adds, this is who they choose not to loan to. “The result,” Satter says, “is a complete revival of redlining in a slightly different guise.”
This is why she wasn’t surprised to see the practice she’d studied as a historian (and lived through with her family in the 1950s) re-emerge as front-page news.
One other factor, though, helps explain why contract selling is back again. The demand among buyers who can’t get mortgages is deep. But so is the supply of houses that might accommodate buyers at the moderate end of the market. The foreclosure crisis created a vast stock of vacant homes, many of which have deteriorated through neglect. Steven Brown, an affiliated scholar at the Urban Institute, has shown that the number of homes worth less than $50,000 has been growing:
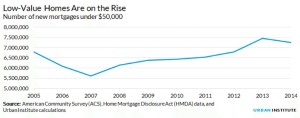
And this has happened as the number of small loans has dwindled:
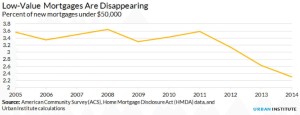
So an investor who has bought up thousands of distressed foreclosures for $10,000-$20,000 a piece has to get creative. These properties need expensive repairs, meaning there likely isn’t much profit in repairing and renting them. They aren’t likely to appreciate much over time in stagnant markets like Detroit or Akron, so an investor can’t simply sit on them waiting for a recovery. And these homes can’t easily be sold at a profit to buyers — even with some modest flipping — because buyers in this market can’t get mortgages.
Contract lending, in other words, is just about the most profitable thing an investor could do with these homes. And that opportunity is colliding right now with a time of desperation for would-be buyers.
One way to look at this situation — today or in the 1950s — is that a market failure exists. Something is not working right in the world of legitimate home lending that’s causing families to reach for dubious alternatives, and that’s prompting dangerous models to proliferate. Satter, though, doesn’t see it this way.
“It’s a market success,” she says, viewed from the standpoint of the investors. “They figured out a great way to make a huge amount of money in this situation.”
As for market failures, she says, maybe we should rethink the term. “If you’re looking at how a market works, this is how it works – people saw an opportunity, they came in and grabbed it,” she says. “The market doesn’t care about fair housing for people, or that families need a place to live.”
And that is the other lesson of history that is repeating itself.
Emily Badger is a reporter for Wonkblog covering urban policy. She was previously a staff writer at The Atlantic Cities. Follow @emilymbadger